
What is the Format of a Video File?
Answer: The format of a video file refers to the structure and encoding used to store and compress video data.
A video file format consists of two main parts: container formats and codecs.
Container formats are like the envelope that holds the video. They keep everything together, including the video, audio, subtitles, and any extra information. Common examples include MP4, AVI, and MKV. MP4 is very popular for online videos because it offers a good balance of quality and file size.
Codecs are the tools that compress and decompress the video and audio data inside the container. They determine how the video is stored and how well it plays back. Popular codecs include H.264 and H.265. First of all, H.264 is widely used because it produces high-quality video while keeping the file size small. Then, H.265 offers even better compression but may not work on older devices.
In short, the format of a video file is a combination of its container and codec, which together decide how the video is stored and played.

7 Most Common Video File Formats
These are the most popular types of video file formats: MP4, WMV, MOV, AVI, WEBM, AVCHD, FLV.
Join me, and let’s break down each video format.
1. MP4
MP4 (MPEG-4 Part 14) is one of the most popular video file formats. It’s widely used for online video streaming and playback due to its high compression efficiency, which keeps file sizes relatively small while maintaining good quality.
MP4 supports a variety of codecs, including H.264 for video and AAC for audio, making it compatible with most devices and platforms, including smartphones, tablets, and web browsers.
2. WMV
WMV (Windows Media Video) is a video format developed by Microsoft. It is primarily designed for streaming on Windows-based systems and offers good compression rates. While WMV files are smaller in size, they are best suited for playback on Windows devices. Some versions of the format can be less compatible with non-Windows systems, so users may need specific software to play these files.
3. MOV
MOV is a file format developed by Apple for its QuickTime Player. It is commonly used for high-quality video files and can contain multiple tracks for video, audio, and text (such as subtitles). MOV files are often used in professional video editing because of their ability to preserve high-quality video.
However, they may be less compatible with non-Apple devices without additional software.
4. AVI
AVI (Audio Video Interleave) is an older video file format created by Microsoft. It supports high-quality video and audio and can contain multiple streams of video and audio data.
While AVI files typically provide better quality, they tend to have larger file sizes compared to more modern formats like MP4.
They are widely compatible across various platforms but may require specific codecs for playback.
5. WEBM
WEBM is an open-source video format developed primarily for web use. It is designed for efficient streaming and is compatible with HTML5.
WEBM supports the VP8 and VP9 video codecs and the Vorbis and Opus audio codecs. This format is commonly used for video content on websites and is supported by most modern web browsers, making it a popular choice for online video applications.
6. AVCHD
AVCHD (Advanced Video Coding High Definition) is a format used for recording high-definition video, primarily by consumer camcorders.
It supports resolutions up to 720p and 1080p and uses H.264 compression, which allows for high-quality video in smaller file sizes. AVCHD files are typically used for professional video production and may require specific software for editing and playback.
7. FLV
FLV (Flash Video) is a format originally created for Adobe Flash Player (discontinued). It is commonly used for online video streaming and is optimized for delivering video content over the internet. FLV files are compact and allow for good quality at relatively low bitrates.
However, with the decline of Flash technology, FLV is becoming less common, and many platforms have transitioned to HTML5 video formats.

Components of Video Formats
Video formats combine resolution, aspect ratio, and bitrate to define video quality, size, and display shape. They also include codecs and containers (like MP4 or MOV) for compression and compatibility across platforms.
Let’s break down each component.
1. Resolution
Defines the clarity and detail of a video, typically measured in pixels (e.g., 1080p, 4K).
Higher resolutions offer better quality but require more storage.
2. Aspect Ratio

The proportional relationship between width and height, such as 16:9 (widescreen), 4:3, or 9:16 (vertical).
The aspect ratio affects how the video displays on different screens.
3. Frame Rate
The number of frames per second (fps), which impacts how smooth or cinematic a video looks. Common frame rates include 24fps, 30fps, and 60fps.
4. Bitrate
Refers to the amount of data processed per second, usually measured in Mbps. Higher bitrates improve video quality but increase file size.
5. Codec
The software used to compress and decompress video files, such as H.264 or H.265. Codecs impact file size, quality, and compatibility.
6. Container
Also known as the file format (like .mp4, .mov, .avi), the container holds the video, audio, and other data streams, affecting compatibility with different devices and platforms.
7. Audio Format
The format for audio within the video, such as AAC or MP3. Audio quality is often influenced by sample rate and bitrate, impacting overall sound clarity.
Differences: Video Formats vs Codecs
Key difference
Video formats define how content is structured and stored in a file, while codecs determine how the actual data within the file is compressed and decompressed, impacting file size and quality.
But let’s dig deeper!
1. Video Formats (Containers)
- Definition: A video format, also known as a container, is a file structure that holds various elements of a video, including the video stream, audio stream, subtitles, and metadata.
- Examples: Common formats include MP4, MOV, AVI, and MKV.
- Purpose: The container organizes and stores all elements, enabling compatibility with players and devices. It determines where the video can be played but doesn’t directly impact the compression or quality.
- Flexibility: Containers can hold different codecs for video and audio, so a single format like MP4 can support multiple codecs (e.g., H.264 for video and AAC for audio).
2. Codecs
- Definition: A codec is software that compresses and decompresses video and audio data. It influences how data is encoded to balance quality and file size.
- Examples: Popular video codecs include H.264, H.265 (HEVC), and VP9. Audio codecs often used in video files include AAC and MP3.
- Purpose: Codecs optimize the video by reducing file size while maintaining quality, making it easier to stream and store.
- Quality and Compression: The codec directly affects video quality, bitrate, and storage efficiency. Some codecs are optimized for higher quality, while others are designed to compress video for streaming.
Best Video Format by Platform
| Platform | Format | Aspect Ratio |
|---|---|---|
| MP4 | 9:16 (Stories/Reels), 1:1 or 4:5 (Feed) | |
| MP4 | 16:9, 4:5 (Vertical) | |
| YouTube | MP4 | 16:9 |
| TikTok | MP4/MOV | 9:16 |
| MP4 | 16:9 or 9:16 (Vertical) | |
| Snapchat | MP4/MOV | 9:16 |
| TV (Broadcast) | MOV/MP4 | 16:9 |
| MP4 | 1:1 or 9:16 |
1. Instagram
- Recommended Format: MP4
- Specs: 1080 x 1920 for Stories and Reels, 1080 x 1080 for Feed
- Aspect Ratio: 9:16 for Stories/Reels, 1:1 or 4:5 for Feed
- Frame Rate: 30fps
- Codec: H.264 with AAC audio
2. Facebook
- Recommended Format: MP4
- Specs: 1080p or 1280 x 720
- Aspect Ratio: 16:9 for wide, 4:5 for vertical
- Frame Rate: 30fps
- Codec: H.264 with AAC audio
3. YouTube
- Recommended Format: MP4
- Specs: 1080p (1920 x 1080) or 4K
- Aspect Ratio: 16:9
- Frame Rate: 24fps or 30fps
- Codec: H.264 or H.265 for higher resolutions
4. TikTok
- Recommended Format: MP4 or MOV
- Specs: 1080 x 1920
- Aspect Ratio: 9:16
- Frame Rate: 30fps
- Codec: H.264 with AAC audio
5. LinkedIn
- Recommended Format: MP4
- Specs: 1080 x 1920 for vertical, 1280 x 720 for horizontal
- Aspect Ratio: 16:9 or 9:16 for vertical
- Frame Rate: 30fps
- Codec: H.264 with AAC audio
6. Snapchat
- Recommended Format: MP4 or MOV
- Specs: 1080 x 1920
- Aspect Ratio: 9:16
- Frame Rate: 30fps
- Codec: H.264 with AAC audio
7. TV (Broadcast)
- Recommended Format: MOV or MP4
- Specs: 1920 x 1080 (HD) or 3840 x 2160 (4K)
- Aspect Ratio: 16:9
- Frame Rate: 30fps or 60fps
- Codec: H.264 or ProRes for high quality
8. WhatsApp
- Recommended Format: MP4
- Specs: 640 x 480 (standard) or 720 x 1280 (higher quality)
- Aspect Ratio: 1:1 or 9:16
- Frame Rate: 30fps
- Codec: H.264 with AAC audio

Choosing the right Video File Format
In this section, I’m aiming to help you pick the right video file format for your needs. Generally, any format is fine with most use-cases, but there are some exceptions.
These exceptions will make your video stand out from just ‘okay’ to ‘GREAT’. Let’s check them out together!
1. Purpose of the Video
The intended use of your video heavily influences the format you choose. For example, if you’re uploading to social media, you’ll want a format that balances quality and size. In contrast, professional editing may require a higher-quality format.
- Streaming: MP4 is ideal for online platforms like YouTube.
- Editing: MOV or AVI retains better quality for post-production work.
2. Quality vs. File Size
Different formats offer varying levels of quality and file sizes. High-quality formats like AVI can take up more storage space, while formats like MP4 provide good quality without being too large. Consider your storage capabilities and distribution method.
- High Quality: AVI or MOV for maximum detail.
- Efficient Compression: MP4 or WEBM for smaller file sizes.
3. Compatibility
Ensure that the video format is compatible with the devices and software your audience will use. MP4 is widely supported across various platforms, making it a safe choice for most situations. In contrast, formats like WMV are best suited for Windows environments.
- Versatile Format: MP4 works on almost all devices.
- Limited Compatibility: WMV may require specific software to play.
4. Target Audience
Consider the technical capabilities and preferences of your audience. If your viewers will access the video on multiple devices, MP4 is a reliable option. Tailor the format to fit the audience’s needs for better engagement.
- Widespread Use: MP4 is user-friendly for various devices.
- Technical Audience: Specialized formats may suit niche groups better.
5. Editing Requirements
If significant editing is involved, choose a format that allows for easy manipulation without losing quality. Formats like MOV or AVI support higher-quality video and audio for effective post-production. This ensures a smoother editing process.
- Edit-Friendly Formats: MOV or AVI retain detail during editing.
- Compression Impact: Lower quality can result from excessive compression.
6. Playback Needs
For videos intended for online playback, choose formats optimized for web delivery. MP4 and WEBM are designed for fast loading and smooth playback across browsers. This is crucial for viewer retention.
- Web Optimization: MP4 and WEBM enhance online viewing experiences.
- Loading Times: Faster formats reduce buffering and increase engagement.
7. Audio Quality
The audio quality of your video is also essential. Formats like MOV support higher bitrate audio codecs, which improve sound quality. Ensure the audio quality meets the expectations of your audience.
- Superior Audio: MOV often supports better audio codecs.
- Consider Bitrate: Higher bitrate leads to clearer sound.
8. Future-Proofing
Think about the longevity and relevance of the format you choose. Newer formats like HEVC (H.265) and AV1 are gaining popularity due to their efficiency. Opting for these formats can help ensure your video remains accessible in the future.
- Emerging Formats: Consider HEVC or AV1 for better efficiency.
- Staying Relevant: Choose formats likely to remain supported long-term.
Create Videos in the Best File Format with SendShort AI
SendShort simplifies the process of creating videos in the best file formats, ensuring high-quality playback and compatibility across platforms.
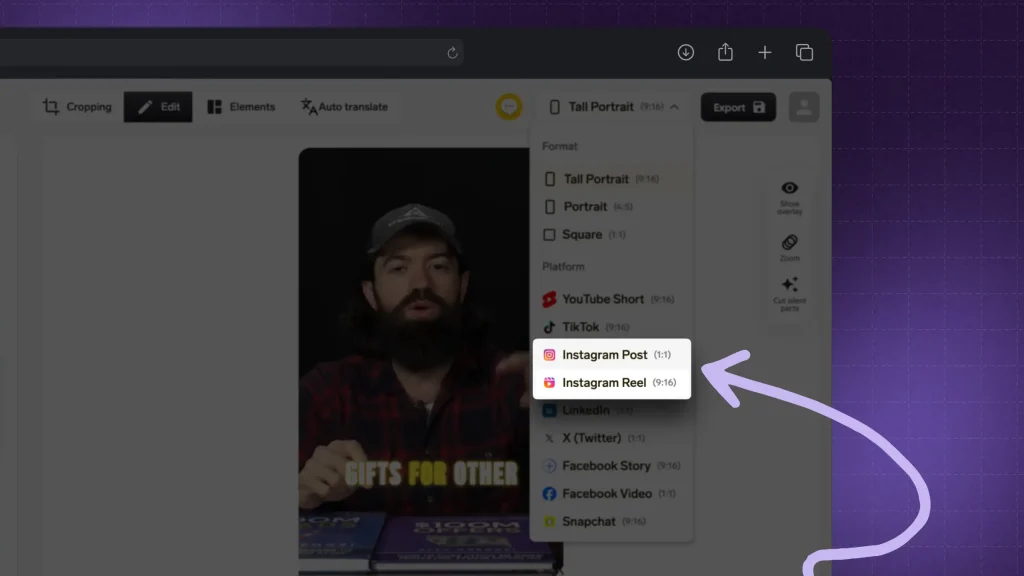
Here’s how SendShort helps you optimize video formats:
- Platform-Specific Formatting: SendShort offers export options optimized for popular platforms like Instagram or YouTube Shorts so your video files meet each platform’s quality and size requirements.
- High-Quality File Options: SendShort lets you export videos in formats like MP4, ensuring smooth playback on most devices and preserving video clarity.
- Flexible Compression: Maintain quality while reducing file size, making your videos load faster without sacrificing visual appeal.
With SendShort, you can produce videos in the ideal format for both quality and compatibility, enhancing your content’s reach and playback experience.

Frequently Asked
1. How many formats of videos are there?
There are numerous video file formats available, with the most common ones including MP4, AVI, MOV, WMV, WEBM, FLV, and AVCHD. Each format serves different purposes and offers varying levels of quality, compression, and compatibility.
2. What are the types of video formats?
The main types of video formats include:
- MP4 (MPEG-4 Part 14): A widely used format for streaming and storing video due to its efficient compression and high compatibility across devices.
- AVI (Audio Video Interleave): An older format that supports high-quality video and audio but generally results in larger file sizes.
- MOV: Developed by Apple, this format is used for high-quality video and is commonly associated with QuickTime Player.
3. Which format is best for video?
MP4 is the best format for videos (regardless of the use-case).
The best video format often depends on your specific needs, but MP4 is generally considered the most versatile choice. It offers a great balance between quality and file size, making it ideal for online streaming, playback on various devices, and sharing on social media.
For professional editing or high-quality productions, MOV or AVI might be better options due to their ability to retain higher video quality. Ultimately, consider the purpose of your video and your audience’s needs when selecting the best format.
Thanks a lot for reading this,
David Ch
Head of the Editing Team at SendShort







