
This guide clear everything once and for all: captions vs subtitles.
In just ~3 mins, my goal is to explain the differences properly so you don’t have ask ChatGPT or Google ever again.
Key Takeaways: Captions vs Subtitles
Captions = everything audible.
Subtitles = dialogue only.
That is the shortest, most accurate explanation you’ll find online. Here’s a 2-sentence explanation as well:
- Captions display all audio elements, including spoken dialogue and sound effects, for those who may be deaf or hard of hearing. They often include non-verbal cues like [music playing] or [door slams].
- Subtitles focus only on translating or transcribing spoken dialogue. They are typically used when viewers don’t understand the language of the dialogue or need a text version of what’s being said.
This table should answer 95% of your questions:
| Aspect | Captions | Subtitles |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | For viewers who are deaf or hard of hearing | For viewers who don’t understand the spoken language |
| Content | Includes all audio elements (dialogue, sounds) | Only transcribes or translates spoken dialogue |
| Non-verbal Sounds | Describes sound effects, music, background noise | Excludes non-verbal sounds |
| Language | Typically in the same language as the audio | Often in a different language than the audio |
| Placement | Can be positioned anywhere on screen (to avoid blocking visuals) | Usually at the bottom of the screen |
| Synchronization | Timed with audio for hearing-impaired viewers | Timed with speech for translation or clarification |
| Usage Context | Accessibility-focused (hearing issues) | Language comprehension (translation or assistance) |
These are the core differences between captions and subtitles.
With this being out of the way, let’s take them break down each aspect of captions and subtitles.
The Basics: Captions & Subtitles
1. What are Captions?
Answer: Captions are text overlays in videos that display spoken dialogue or important sounds.
They help viewers understand the content, especially in noisy environments, or for those who are deaf or hard of hearing.
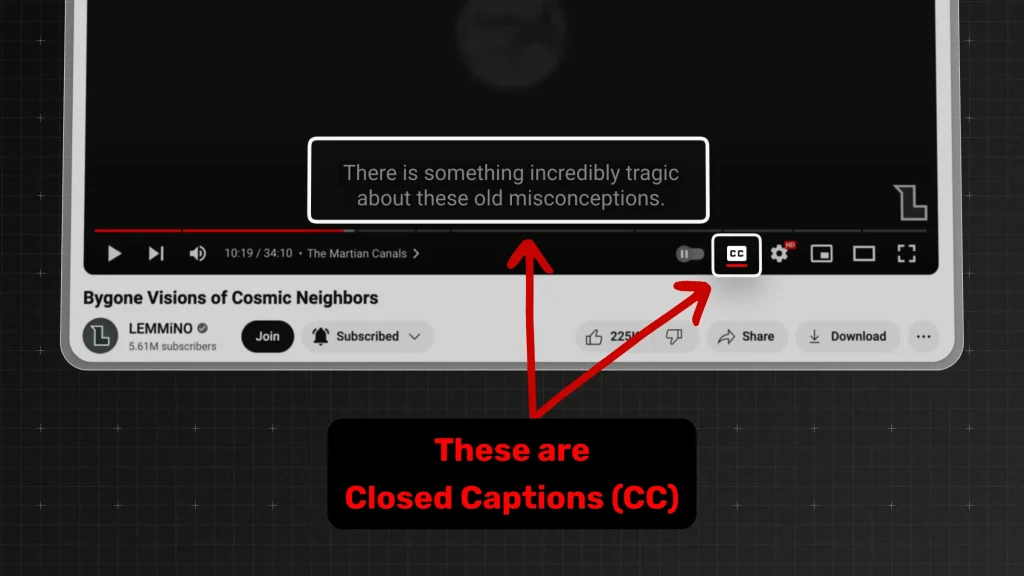
- Captions can be closed (optional to turn on) or open (always displayed).
- They’re commonly used in video content on platforms like YouTube, social media, and streaming services.
2. What are Subtitles?
Answer: Subtitles are text translations or transcriptions of spoken dialogue in videos.
They’re primarily used to help viewers understand content in a different language or when the audio isn’t clear.
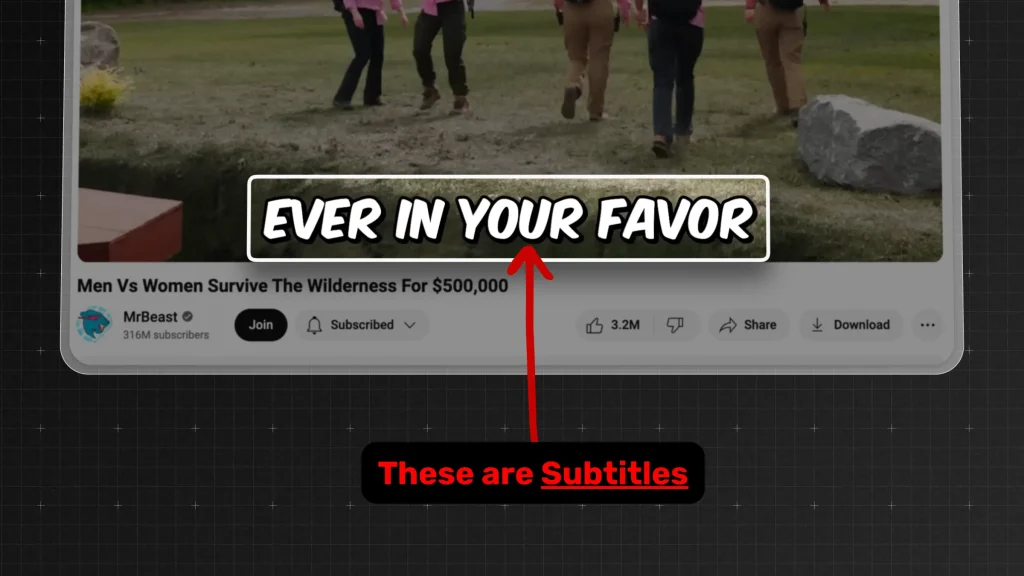
- Unlike captions, subtitles don’t usually describe non-speech elements like sound effects or music.
- They appear in films, TV shows, and online videos to help reach a global audience.
Great, now let’s se…
3. When to Use Which?
Short Answer: Captions are more inclusive for accessibility, while subtitles focus on language barriers.
Take a look at this table:
| Criteria | Captions | Subtitles |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Displays spoken dialogue and non-speech sounds (e.g., music, sound effects) | Translates spoken dialogue into a different language |
| Focus | Both speech and important sounds | Speech only |
| Accessibility | Designed for viewers who are deaf or hard of hearing | Designed for viewers who understand a different language |
| Common Uses | TV shows, videos, and movies to enhance accessibility | Foreign films, international content, or multilingual videos |
| Environment Suitability | Noisy environments or situations where audio isn’t clear | When language translation is needed |
Captions should be used when you need to display both spoken dialogue and important non-speech sounds, such as background noises, music, or sound effects. They’re essential for accessibility, ensuring that people who are deaf or hard of hearing can fully understand the content. Captions are also useful in noisy environments where audio might not be clear.
Subtitles should be used to translate spoken dialogue from one language to another. They focus purely on speech and do not include non-speech sounds. Subtitles are ideal for making content accessible to viewers who speak a different language but don’t need extra audio descriptions.
TOP 4: Differences between Captions & Subtitles
Main Differences: Subtitles transcribe only spoken dialogue, mainly for viewers who don’t understand the language. Captions include dialogue, sound effects, and other audio cues for the hearing impaired.
Let’s break down each.
1. Transcript
Captions often include a full transcript of both spoken dialogue and relevant non-verbal sounds. Subtitles, on the other hand, provide only a transcription of spoken language.
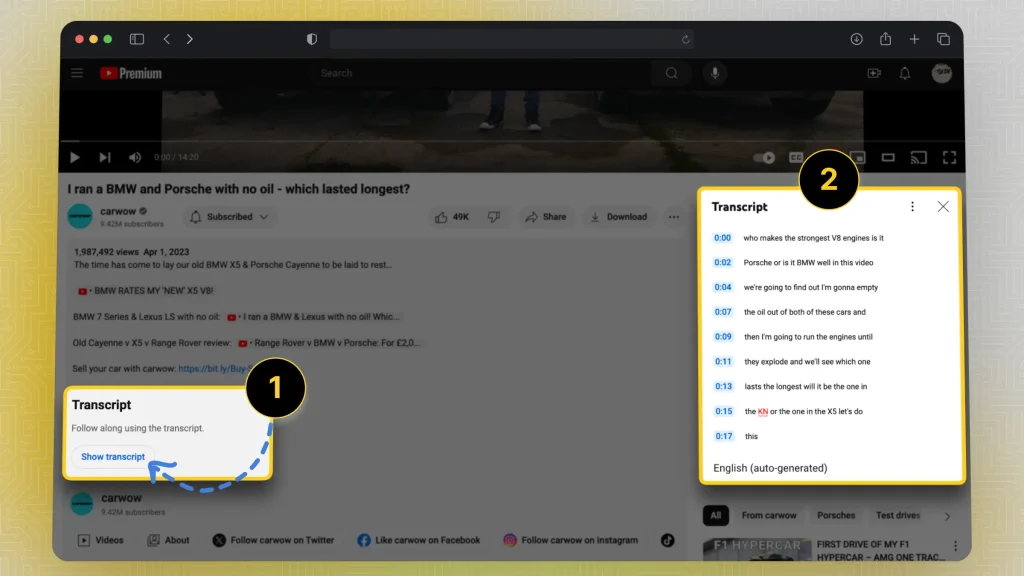
- Captions: Transcribe speech and sounds (e.g., “[door slams]”)
- Subtitles: Only transcribe spoken words.
2. Accessibility
Captions are crucial for individuals who are deaf or hard of hearing (SDH), offering details on all audio elements. Subtitles typically assist those who don’t understand the language but don’t always cater to hearing impairments.
This Chrome Extension is great for accessibility controls:
- Captions: Support hearing-impaired audiences.
- Subtitles: Aid language comprehension, not focused on non-verbal cues.
3. Placement
Captions are often displayed at the bottom of the screen but can move to avoid covering important visuals. Subtitles stay fixed at the bottom of the screen.
- Captions: Flexible placement to avoid obstruction.
- Subtitles: Typically fixed at the bottom.
4. Timing
Captions are synced with both dialogue and other sounds, ensuring viewers get a real-time experience. Subtitles focus on matching the spoken words only.
- Captions: Synced to dialogue and sound effects.
- Subtitles: Synced to dialogue alone.
FAQs
1. Why are subtitles called CC?
Answer: Subtitles are called CC (Closed Captions) because they provide dialogue, sound effects, and speaker info for accessibility.
This term highlights their function of making content accessible to those who are deaf or hard of hearing.
2. Are captions and subtitles the same?
Answer: No, captions include dialogue and non-verbal sounds for accessibility, while subtitles only show spoken dialogue.
3. How do captions and subtitles work?
Answer: Captions display dialogue and sound effects for accessibility, syncing with audio cues. Subtitles show only the spoken words, mainly for language translation.
Thanks a lot for reading this,
David Ch
Head of the Editing Team at SendShort







